A Retail Object Classification Method Using Multiple Cameras for Vision-Based Unmanned Kiosks
In the contemporary landscape of digital automation, Retail Enterprises are aiming for unmanned kiosks or self-checkout systems by integrating sensors and wireless communication tools into their businesses. Retail automation is convenient, and enhances shopping experiences. However, it is costly due to complex sensors, numerous cameras, and high computing demands, thus restricting it to large enterprises.
The paper proposes a vision-based unmanned kiosk that detects retail items using multiple cameras and classifies them using a simple machine learning algorithm at low computational cost.
A significant challenge in product recognition arises from limited detections and the prevalence of both intraclass variations (variations within the same product category) and interclass similarities (similarities between different product categories) in retail items. Existing sensors cannot differentiate between the appearances of objects properly due to a lack of discriminative and exclusively identifiable features.
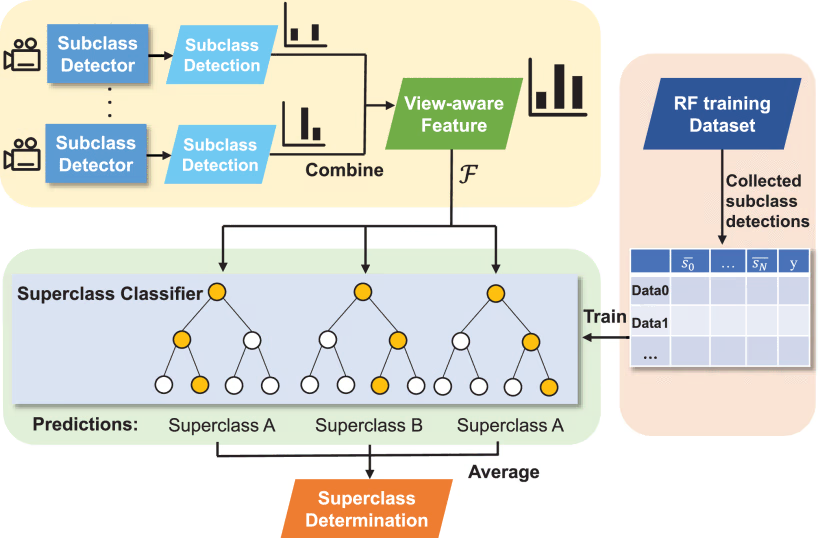
A vision-based unmanned ‘Kiosk’ is constructed with a display rack and an RGB camera sensor installed on the shelf. Operating on CNN principles, detectors are utilized to recognize a product that appears in the input image captured by the camera sensor. A view-aware classification method is introduced alongside a view-based annotation method to address similarity in retail objects and aggregate Multiview detections.
This kiosk mitigates inter-class confusion by deploying multiple cameras, each equipped with a CNN detector, conducting independent detections on its input image. Single objects are categorized into multiple subclasses, forming the basis for training the detection network to enhance view-specific saliency.
The resulting view-specific features are then aggregated to create a view-aware feature, subsequently utilized in training a random forest (RF) superclass classifier. RF excels in calculating feature importance and handling missing values, making it adept at identifying the "informative" viewpoint among multiple subclass detections.
In the view-based annotation approach, objects are subdivided into subclasses, considering intra-class variations for the top, middle, and bottom sections. The original object category serves as the superclass, enhancing recognition by distinguishing clear appearances from ambiguous ones.
Each camera, equipped with subclass detectors through the view-based annotation method, generates view-specific features. The classifier uses these features to accurately identify and classify objects through the annotation method, contributing to creating a comprehensive view-aware classification feature. The classifier determines the final superclass of an instance, optimizing object recognition across diverse viewpoints utilizing these features.
The prototype of this multi-camera kiosk collected data points within this framework. The real-world dataset, consisting of 142,420 images depicting the purchase process, incorporates two types of label sets. One set utilizes "view-based" labels through the proposed annotation method, while the second set employs labels annotated using a conventional method. Evaluation of a vision-based unmanned kiosk system using a retail product dataset demonstrates a 33.67% improvement in F1 score over conventional methods. The effectiveness of the process is substantiated by evaluating a real-world dataset with various CNN detectors.
These features enable this Kiosk to predict object categories, considering each viewpoint's significance accurately. While the current focus is on instant image classification, future enhancements may explore temporal information, object tracking, and attention-based techniques.