Using Adaptive Wireless Transmission of Wearable Sensor Device for Target Heart Rate Monitoring of Sports Information
With people becoming more aware of their physical and mental health and active research on the advancements in the healthcare industry, there is a boom in smart wearable devices. The traditional method of primary healthcare and seeking advice from medical personnel or general practitioners are slowly getting replaced by modern wearable sensor devices for continuous monitoring of heartbeats and other health parameters. Portable medical devices, wearable biosensor jackets, smart shirts, wireless patch sensors, and other smart wearable devices have tremendous advantages to the medical smart wearable sensor devices industry.
Adaptive filtering, a system which can adapt to the filter parameters suited to the optimization algorithm, is widely used in digital signal processing. The various adaptive filtering algorithms in place vary in the different filtering operators used. Simple network structure and easy implementation have made LMS adaptive filtering algorithm a popular choice. The development of portable and wearable sensor devices would not have been possible without the advent of wireless communication technology.
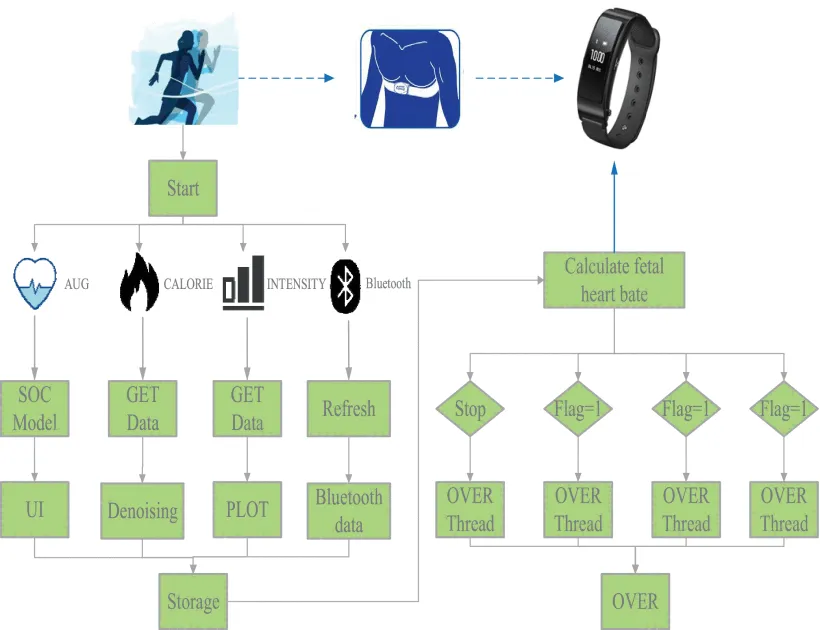
Target heart rate monitoring systems using adaptive filtering need to have real time performance to operate accurately. The Android operating system architecture contains multiple threads in the design architecture. When the Bluetooth of the device in use is ON, the Bluetooth thread is responsible for establishing a connection, data reading and data playing. Next in line is the algorithm thread which is the core of the system. The algorithm thread processes data stored in the first-in-first-out structure from the Bluetooth thread with the help of target heart rate signal noise reduction and target heart rate extraction. The drawing thread and the display thread are then responsible for drawing the graphs derived from the algorithm thread and displaying them to the user. These threads need to be refreshed to display dynamic data to the user.
The target heart rate extraction algorithm mainly uses the direct calculation method and the time windowing method. In the direction calculation method, the time difference between two peaks and the number of cycles in a peak is calculated. But it poses problems in practical applications due to the presence of noise. In the latter method, the number of peaks is calculated in a fixed-length time window and then multiplied with the number of time windows in a minute to represent the target heart rate. An improved algorithm, the automatic weighted average algorithm, is proposed to sharpen the results further.
There are various algorithms used for denoising of the data. Compared to methods such as the EMD decomposition algorithm and wavelet transform, adaptive least square method is most suited. It tracks first target heart rate and second target heart rate effectively as well as it strongly suppresses the noise.
Overall, the target heart rate monitoring system is a success with a scope of improvement in accuracy of data and elimination of noise.